Keyword [Context Encoding]
Zhang H, Dana K, Shi J, et al. Context encoding for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 7151-7160.
1. Overview
1.1. Motivation
- recent works exploit FCN + dilated/atrous Conv and utilize multi-scale features and refining boundaries
- dilated/atrous Conv isolates the pixels from the global scene context
In this paper, in proposed Context Encoding Module
- explore global contextual information
- selectively highlight class-dependent featuremaps
- improve performance with only marginal extra computation cost
- 14 layers network
- extend the Encoding Layer to capture global feature statistics for understanding semantic context
1.2. Question
Is capturing contextual information the same as increasing the receptive filed size?
1.3. Contribution
- Context Encoding Module incorporating Semantic Encoding Loss (SE-loss). SE-loss can regularize training, enforce network learning of semantic context
- EncNet. 3.5M parameters
2. Methods

2.1. Context Encoding
- encoder semantics. output of encoding layer
- apply aggregation instead of concatenation
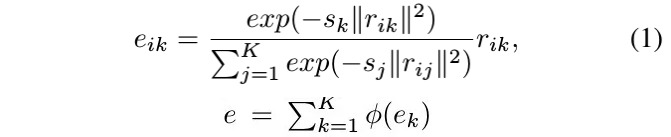
2.1.1. Feature Attention
- FC + Sigmoid

2.1.2. SE-Loss
- unlike per-pixel loss, SE-loss consider big and small objects equally
2.2. Context Encoding Network
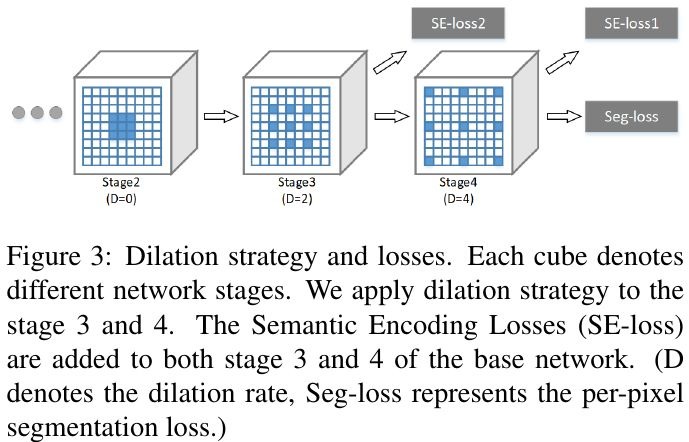
- pretrained Dilated Residual Network (dilated strategy at stage 3 and 4)
3. Experiments
3.1. Details
- output size 1/8
- bilinear upsample 8 times of prediction
- random shuffle training samples, discard last mini-batch
- random flip + random scale (0.5~2) + random rotate (-10~10) + crop to fix size if padding needed
- Implement Synchronized Cross-GPU BN in Pytorch using NVIDIA CUDA & NCCL toolkit
- K = 32
- batchsize 16
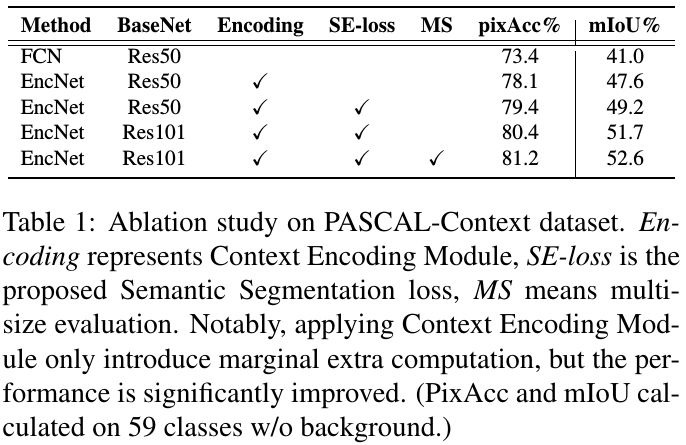
3.2. Comparison


3.3. Ablation Study